TCV 90/91, opposite Patient Mitra Pharmacy, Opposite Ram Manohar Lohiya Hospital, Vibhuti Khand, Gomti Nagar, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh 226010
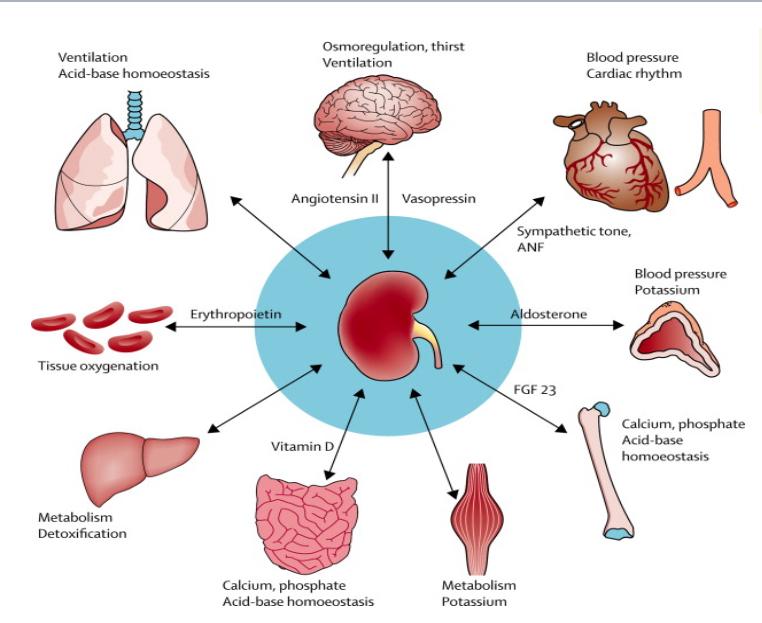
Clinical nephrology is the branch of medicine dedicated to diagnosing, managing, and treating diseases of the kidneys and related systemic conditions. It focuses on the prevention, detection, and management of kidney dysfunction, electrolyte imbalances, and associated complications
Key Areas of Clinical Nephrology
1. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
2. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
3. Glomerular Diseases
4. Hypertension
5. Electrolyte and Acid-Base Disorders.
6. Systemic Diseases with Renal Involvement
7. Other kidney disorders.
8. Renal Transplantation
TCV 90/91, opposite Patient Mitra Pharmacy, Opposite Ram Manohar Lohiya Hospital, Vibhuti Khand, Gomti Nagar, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh 226010
nephrosapians@gmail.com
Copyright @ 2024 || Designed With 